How to Find Network Vulnerabilities? A Rookie Guide

A vulnerability is a technical defect or a shortcoming in the system that a cybercriminal could exploit to gain unauthorized entry and illegal access to sensitive data and transactions. The company’s and its customers’ security and safety are jeopardized by network weaknesses.
Cyber-resilience experts at Bloo Solutions, a Springfield-managed IT services company, opine that the vulnerability or defect in network systems may be due to flawed design and error-prone procedures. Defective network construction, laxity in operations, or shortcomings in network maintenance add to the vulnerabilities.
The term vulnerability refers to the weakness in the hardware and software that exposes the company to a cyber attack. Risk refers to the potential for vulnerabilities to inflict financial pain, physical damage, or asset destruction.
Five Network Vulnerabilities That Compromise Systems Security and Data Safety
There are several kinds of network vulnerabilities that can compromise systems security and data safety. We have listed the top five for a better understanding of things.
Weak Password Protection Protocols
It’s commonplace for hackers to employ brute-force methods to crack open systems vulnerabilities and weak passwords open the floodgates to sensitive data. After repeated failures, locking the system and prolonging the login attempts adds a more muscular protection layer.
Unencrypted, Unsecured, Unprotected Data
When data is unencrypted, you make it easier for cybercriminals to steal sensitive information. Encryption becomes the ideal solution. Even if data is stolen, it’s difficult for hackers to make sense of unintelligible gibberish until they decode it.
Unpatched Software and Outdated Operating Systems
Unpatched software was the primary entry point for ransom attackers in 2021. Software vendors identify bugs in the system and write additional code to patch up the vulnerability. If the OS runs unpatched, you provide a fertile ground for attackers to run malicious codes that exploit weaknesses.
Open Ports and Services
Ports enable internet-facing services and applications to allow communications between devices, freedom that’s at the core of the net surfing experience. Sometimes the administrator might leave a port open unintentionally, or systems reconfiguration might do the same, and the change remains undetected.
Insecure Wireless Networks
Without a formal login or screening protocol, an insecure wireless network is an open invitation to an intruder within an approachable radius to capture and transmit sensitive data. The most common danger resulting from insecure networks is identity theft and financial fraud.
What is Network Vulnerability?

A network vulnerability is a flaw or weakness in organizational procedures, hardware, or software that, if exploited by a threat, could lead to a security breach.
Hardware, firmware, software, and human vulnerabilities are the different types of network vulnerabilities. If any of these entities are not handled correctly, it will be simple to hack into your network. Network vulnerabilities fluctuate in complexity and severity since every business is unique.
By continually evaluating security rules and developing protocols and procedures, it’s critical to be aware of all vulnerabilities in order to stop recurrent network vulnerabilities. It is essential to understand the causes of network vulnerabilities and learn how to prevent them in order to be aware of the hazards.
According to some reports, only 14% of small businesses know how to tackle situations like network vulnerabilities.
The Four Components of Network Vulnerability Assessment
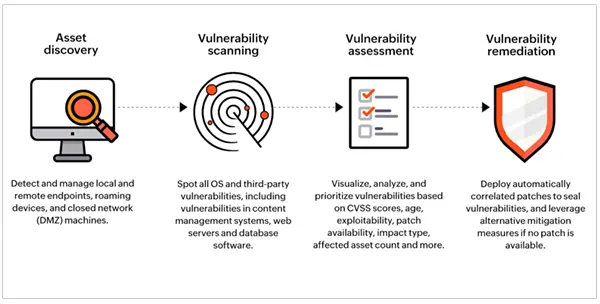
Assessment of the network vulnerability is quite significant. It consists of four components let’s explore each one of them in detail.
Determining the Scope of the Assessment
The most critical stage is where a decision is made regarding the extent of the testing environment. The scope of testing requirements decides the kind of tools you deploy for vulnerability scanning and the company resources you need.
Moving to Data Collection
The assessment has to cover three broad areas, the network architecture (whether terrestrial-based or cloud-native), the devices that plug into the network, and OS base and systems configuration. Scanning will draw information from all three levels.
Analysis and Reporting Vulnerability and Risk
After scanning the network and collecting information regarding weaknesses, it’s time for automated vulnerability scanners to identify and record vulnerabilities. The findings come out as a report that analyses each vulnerability with its risk weightage and suggests remedial action.
Remediation as a Policy Intervention
Remedial measures involve the systems administrators, network coordinators, and company directors, as some significant interventions might require policy changes.
Why Do You Need Network Vulnerability Assessment?

Your company relies heavily on its IT infrastructure, but it also depends on computers and other electronic devices that can be attacked with phishing scams.
An organization can learn more about any security flaws in its surroundings through a vulnerability assessment. It also offers guidance on how to evaluate the risks brought on by those flaws. Additionally, it requires action so that you can take precautions against malicious hackers.
Best Practices That Prevent Network Disruption And Data Breaches
Getting third-party managed IT assistance in rooting out network vulnerabilities is essential because the IT architecture, systems, and procedures undergo professional vetting.
The immediate takeaway of adopting network security practices is increased cyber-resilience, zero trust network access, and top-notch safety. Let’s run our eyes over a few of them.
- The business is equipped to combat cybercrime and safeguard its database when software defects are swiftly patched and system flaws are routinely fixed.
- Strengthening passwords and passphrases and exercising greater control over administrative and employee access rights makes it more difficult for intruders to break systems.
- With so many employees working remotely through external devices in the post-pandemic scenario, two-factor authentication improves the security posture. The 2FA requires multiple channels to authenticate the user, such as using a password, entering OTP received on a mobile device, and biometric scanning to define features.
- Transforming readable data into its encrypted form gives data more robust protection against hacking. Even if the information is stolen, it’s difficult to decode the unidentifiable gibberish.
- A reconfiguration of Admin-level privileges and additional layers of protection in authorizing personnel to handle sensitive data prevents data from falling prey to hackers.
Conclusion
We discovered that networks experience vulnerability problems and that the vulnerability threat is detected and examined by a systematic scanning process.
Along with that, we realized that vulnerability scanning for networking systems’ hardware and software occurs at different levels, addressing the difficulties at each one.
Finally, we understand how crucial vulnerability scanning, investigation, reporting, and correction are to the protection of sensitive data as well as the cybersecurity of the firm.
What distinguishes network vulnerability scanning from web application vulnerability scanning?
The latter is confined to the specific application under scrutiny, whereas the former encompasses all applications and services operating within a network.
What are the three classifications of network service vulnerabilities?
At the most elevated level, network security vulnerabilities can be categorized into three extensive classifications, namely hardware issues, software issues, and human security issues.
Can you suggest some free tools for network vulnerability assessment?
There are a handful of tools available for this in the market, you can use Wireshark or Nessus.