Oral Glucose Tolerance Test
The Glucose Tolerance Test (GTT) or Oral Glucose Tolerance Test (OGTT) is a method for diagnosing insulin resistance or diabetes mellitus in a person. It is a more significant indicator of diabetes as compared to normal finger prick testing. To live a healthier life, one must keep a check on their vitals like blood sugar levels, & a GTT test is the way to go.
What is meant by an OGT test?
This test is done to determine whether a person’s body experiences any trouble while metabolizing the consumption of glucose or carbs. In this test, the patient is given a glucose drink and then the measurement of blood sugar level is done before and at intervals following the consumption of a glucose drink.
Why is OGTT Test Done?
The OGTT measures how the body is capable of managing sugar levels after a meal. Glucose is a type of sugar formed when carbs (taken from foods) get broken down by the body. Few of this sugar is utilized for the purpose of energy; while the rest is stored for future use.
Insulin and glucagon are two hormones that control the amount of sugar in a person’s blood. If a person has an excess of these, his or her pancreas secretes insulin in order, to assist the cells in storing and absorbing the sugar.
In a person, if a slight of these hormones is found, then the pancreas secretes glucagon to facilitate the release of this stored sugar back into the bloodstream. Under standard conditions, the body could sustain an ideal balance of blood sugar.
On the other hand, if body parts are weakened, sugar starts accumulating rapidly, giving rise to high blood glucose (hyperglycemia) or diabetes.
It is a highly sensitive test that is done to detect abnormalities that other tests might miss. OGTT is recommended for the following purposes:
- For Pre-Screening and diagnosis of early diabetes
- Screening and diagnosis of gestational diabetes
- Screening and diagnosis of type 2 diabetes
- Diagnosis of beta-cell dysfunction (there is no secretion of insulin)
- It helps in the diagnosis of reactive hypoglycemia (a condition in which the glucose levels fall after consuming food)
- Early diagnosis of some rare problems that have an impact on the metabolism of carbs (for example, hereditary fructose intolerance)
- Diagnosis of acromegaly (a condition in which the pituitary gland becomes overactive).
How is the OGTT Test Done?
The OGTT test involves some vital steps that are mentioned below:
- A person is asked not to have anything, or drink certain fluids, for a maximum of 8 to 12 hours prior to the test. Also, a person is asked not to take any medicines before the test, only as per the doctor’s guidance.
- A person’s blood is taken initially to evaluate his or her blood glucose level before the test.
- The next step is to consume a very sweet relishing sugar drink.
- Next, blood samples are taken at regular intervals of half an hour or one hour or a single test after 2 hours.
- This test can take up to 3 hours.
Types of OGTT Test
The OGTT method may differ significantly depending on the objectives of the test. The amount of the oral glucose solution may also vary with the timing and number of blood draws needed. Even, there may be differences in which a low-carb meal can be suggested.
Two standard variations can be utilized for screening and diagnostic purposes:
- A 2-hour OGTT, in which there are two blood draws. This test diagnoses diabetes or prediabetes in non-pregnant adults as well as children.
- A 3-hour OGTT, in which there are four blood draws. This test screens for gestational diabetes.
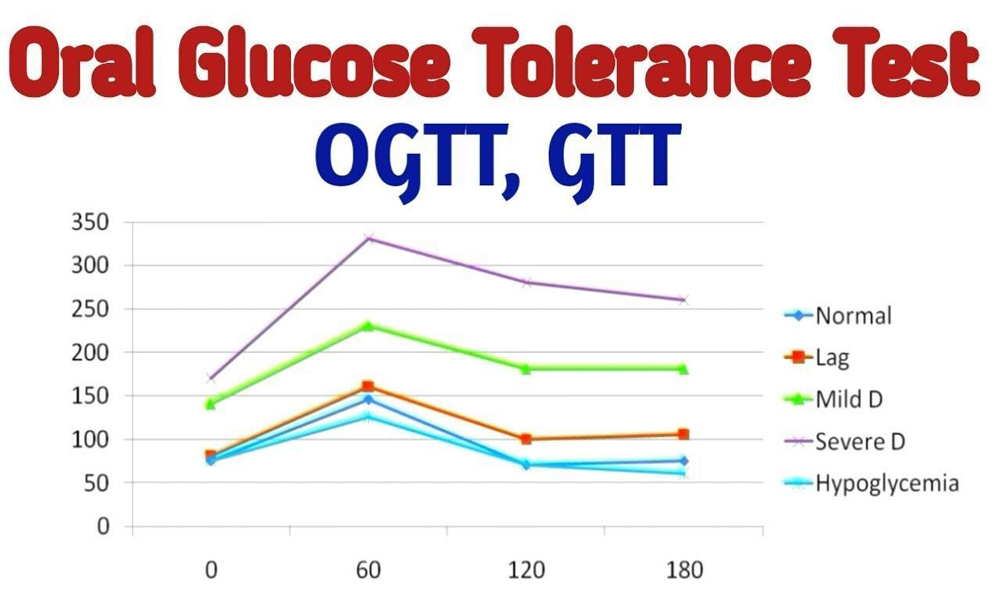
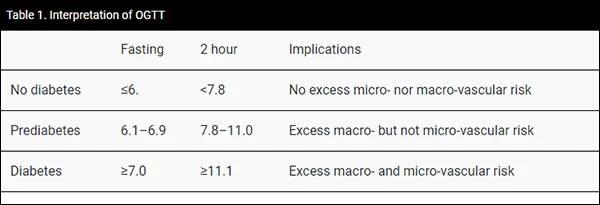
What Should the Perfect OGTT Results Be?
The perfect range of OGTT may differ among people. Let’s look at some of them in detail.

Non-diabetics
- Fasting value (prior to test): under 6 mmol/L
- At 2 hours: under 7.8 mmol/L
People having an impaired glucose tolerance (IGT)
- Fasting value (prior to test): 6.0 to 7.0 mmol/L
- At 2 hours: 7.9 to 11.0 mmol/L
For people with diabetes
- Fasting value (prior to test): over 7.0 mmol/L
- At 2 hours: over 11.0 mmol/L
What Do These Test Outcomes Indicate?
If a person lies within the impaired glucose tolerance range, he or she is expected to be suggested to adopt certain lifestyle alterations like sleep deprivation.
In certain cases, blood sugar-lowering drugs can be recommended. If a person falls within the diabetic range, it is almost certain that he or she would be recommended anti-diabetic drugs to help his or her body keep their blood sugar levels down.
What OGTT Results Won’t Tell You?
There are many things that won’t be told or reflected in your OGTT reports. Here is a list of a few of them.
- Whether the sample collection was done properly or not.
- It won’t reflect whether the test was carried out properly or not.
- This test does not differentiate between Type 1 and Type 2 diabetes and shows collective scores.
- Does not reflect the future risk of getting diabetic.
These are some bunch of things that are not reflected in your oral glucose report.
What are the Risks Associated With the OGTT Test?
To be precise, there is no risk involved in the OGTT test if you mindfully follow all the instructions given by your doctor. Only in worst case scenario or if you are too unlucky, in that case, you can face issues like:
- Bleeding
- Bruising
- Dizziness or lightheaded
- Infection
- Clotting
Pros and Cons of OGTT Test
There are a handful of pros and cons of the OGTT test. The table below highlights the same.
Why a Woman Should Get Her OGTT Test Done During Pregnancy?
You might have noticed that many pregnant women in your household go through an OGTT test in their second trimester. Ever wondered why? The precise reason for conducting this test is to test whether the soon-to-be mother is having gestational diabetes or not.
During the pregnancy, women might experience some shoot of blood sugar levels, which in most cases recede when they give birth. So, a postpartum diabetes test could be conducted. But during the pregnancy, a woman is advised to reduce intake of sugar and fried food, if gestational diabetes develops.
Final Words
Low and higher sugar levels can turn your life upside down. So it’s best to go through a blood sugar diagnosis test like OGTT every two to three months, to monitor your body levels. It is often said early diagnosis can lessen the body damage caused by these health issues. Moreover, this test provides security in healthcare to patients who might seem confused about the different sugar tests.
- What is meant by an OGT test?
- Why is OGTT Test Done?
- How is the OGTT Test Done?
- Types of OGTT Test
- What Should the Perfect OGTT Results Be?
- What Do These Test Outcomes Indicate?
- What OGTT Results Won’t Tell You?
- What are the Risks Associated With the OGTT Test?
- Pros and Cons of OGTT Test
- Why a Woman Should Get Her OGTT Test Done During Pregnancy?
- Final Words